This is Your Sign to Carry
In 2007, hedge fund manager John Paulson made $4 billion using the carry trade. Today, you can access the same strategy with just $100 and a single click.
What is a carry trade, exactly?
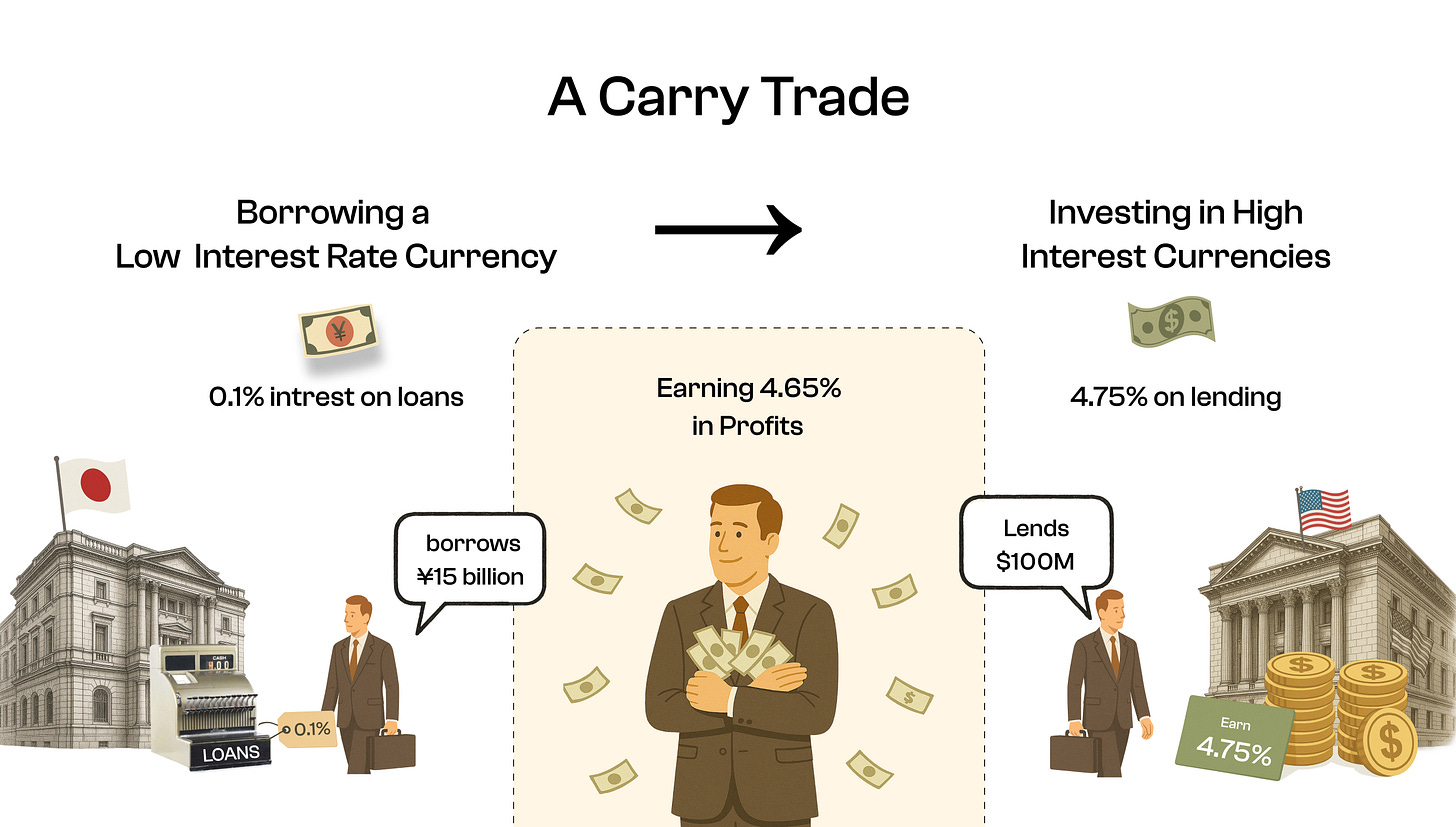
Imagine borrowing money at a low interest rate, then investing it somewhere else with higher returns. The profit you make—the difference between the higher return you earn and the lower cost of borrowing—is called "carry."
It sounds simple, but in traditional finance, only elite institutions could execute this strategy:
Banks and hedge funds establish exclusive relationships with foreign financial institutions
They secure massive credit lines (often $50+ million minimum) backed by premium collateral
They navigate complex legal frameworks and currency regulations
They pay significant fees to prime brokers who facilitate these cross-border transactions
The carry trade has powered global markets for decades, moving over $1.7 trillion across borders in search of yield at its 2007 peak—roughly equivalent to the entire GDP of Italy at the time.
As of April 2025, despite partial unwinding due to BOJ rate hikes to 0.5% and yen appreciation (USD/JPY at 142.17), the carry trade continues to channel substantial funds, likely in the range of $1–$1.5 trillion, through FX and bond markets, driven by Japanese banks’ foreign lending and nonbank intermediaries.
This high barrier to entry kept everyday investors locked out of one of Wall Street's most reliable yield farming trades
That is, until now.
Now this time-tested strategy is being reborn at the internet capital market, aka crypto, creating new opportunities for savvy DeFi investors.
The Japanese Origins
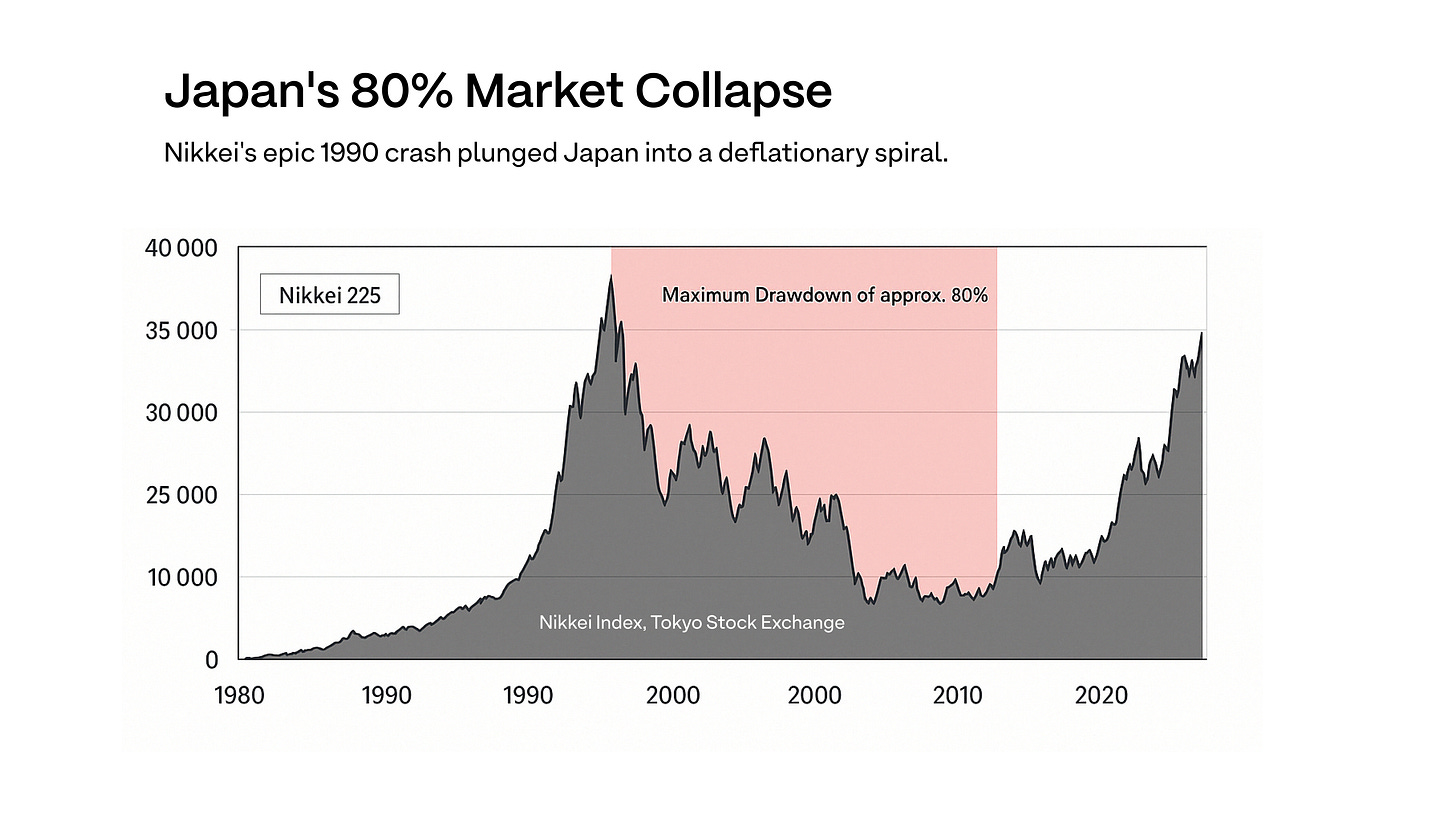
In the 1980s, Japan’s economy boomed, pushing stock and real estate prices sky-high. But by the early 1990s, the bubble burst. Asset values collapsed, borrowers defaulted, and banks began to fail. Japan entered a long slump marked by deflation—falling prices that caused people to delay spending, which hurt growth even more.
To fight this, the Bank of Japan cut interest rates to near zero.
Low interest rates made borrowing money very cheap, encouraging people and businesses to borrow again and spend or invest that money. By making borrowing easier, Japan's central bank hoped to kickstart spending and investment, revitalizing economic growth.
After this, the Bank of Japan kept interest rates near zero for decades. This created perfect conditions for carry traders. Global macro hedge funds (like those run by George Soros and Paul Tudor Jones), investment banks (Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan, Deutsche Bank), and institutional investors borrowed massive amounts of Yen at minimal cost, then converted and deployed that capital across higher-yielding assets worldwide
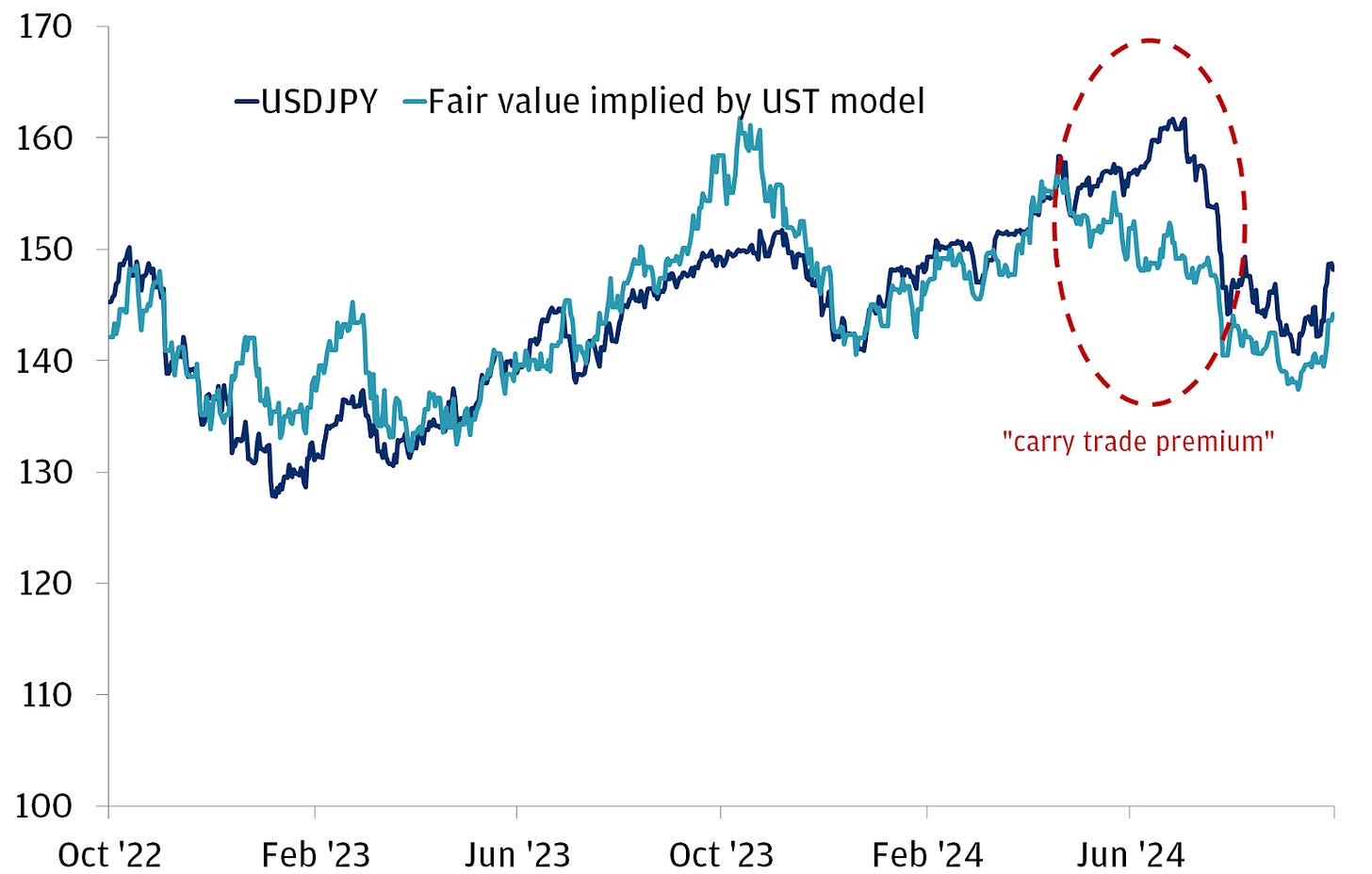
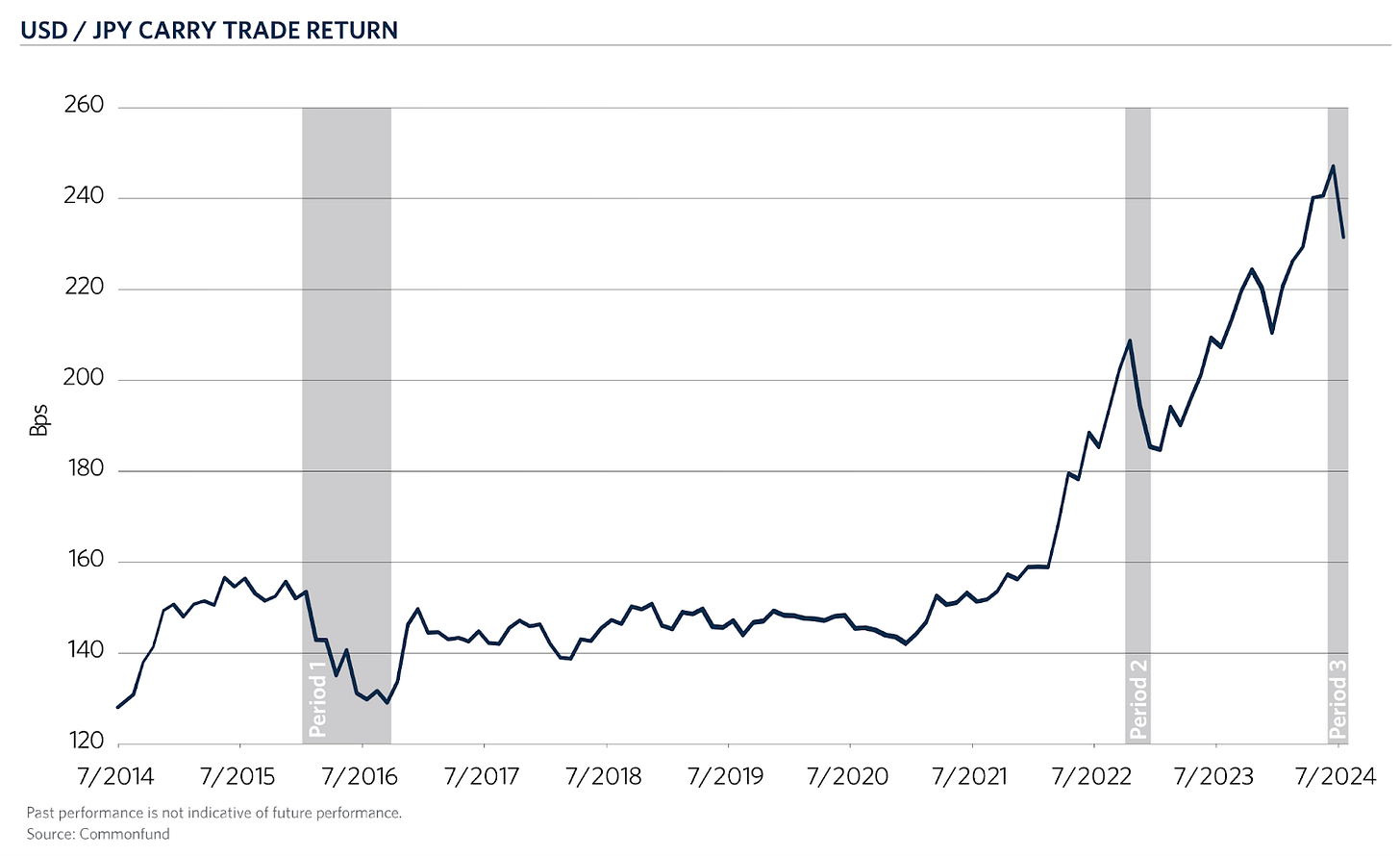
By 2024, Japanese banks had lent over $1 trillion in yen abroad, with much of it routed through offshore hubs like the Cayman Islands. Just the dollar-yen carry trade alone reached $500 billion, according to UBS. Zooming out, Japan’s total foreign portfolio investment—often cited as the broadest measure of yen-funded carry trades—topped $4 trillion by the end of 2024, underlining the massive scale and global reach of this strategy.
Why It Worked (Until It Didn't)
The mechanics of these trades were simple but powerful:
A hedge fund posts $100 million as collateral with a Japanese bank.
→ Borrows ¥15 billion (about $100 million) at 0.5% interest.
→ Converts this to USD, investing it into U.S. Treasury bonds yielding 5%.
→ Net profit per year: around $4.5 million (before any currency risk, i.e, JPY increasing relative to USD).
For decades, this reliable strategy powered global financial flows.
Countries with higher interest rates saw their currencies strengthen as investors rushed in. Emerging markets gained access to cheaper capital. The carry trade became a hidden engine of global finance.
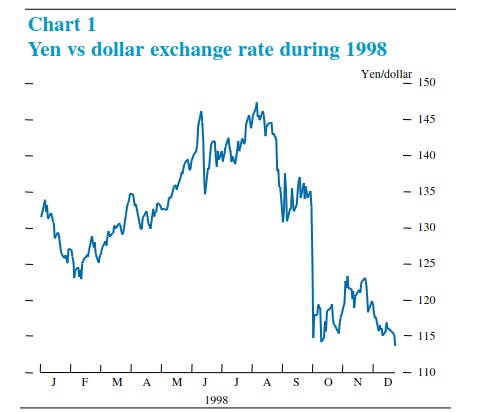
But occasionally, volatility hit. In October 1998, the Japanese Yen surged 17% in just a week, wiping out many carry traders' profits.
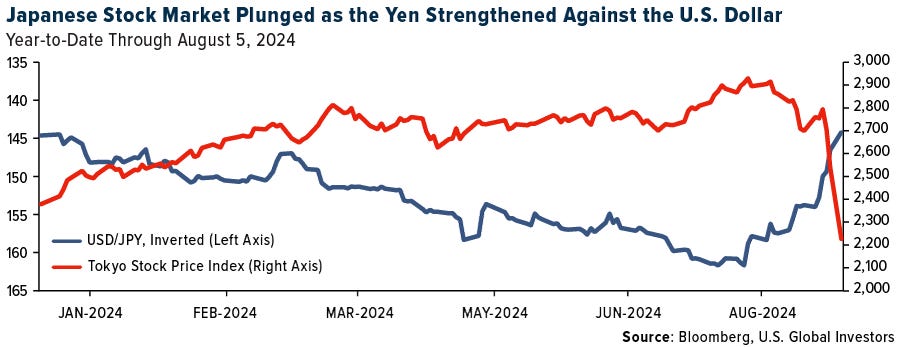
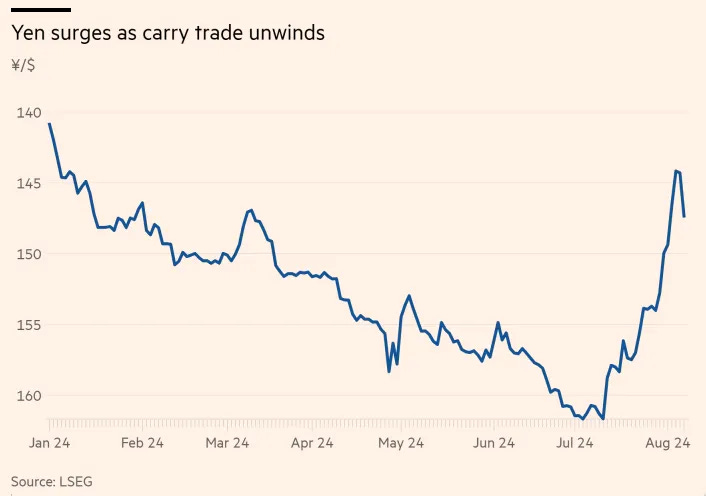
More recently, in July 2024, the Bank of Japan raised interest rates from near-zero to 0.5% after decades of ultra-low rates. This direct increase narrowed the interest rate gap between Japan and the US, making the carry trade less profitable. As a result, traders rushed to unwind their positions, selling dollars to repay their yen-denominated loans. This massive unwinding caused the USD-JPY pair to drop nearly 7% in just days.
By August 2024, as the BOJ signaled further rate increases, more traders exited their positions, pushing the Yen's appreciation to almost 10% against the dollar. This chain reaction:
Higher Japanese rates → smaller yield differential → mass position unwinding by selling USD and buying JPY to repay the loans→ stronger yen
This effectively marked the end of the Yen carry trade era as it had existed for decades. By August 2024, futures positions showed net long on JPY for the first time since 2021—a clear signal the unwinding was underway.
DeFi’s Carry Trade Moment
While traditional finance mourns the end of the Yen carry trade, crypto is building something more powerful, transparent and much more capital-efficient.
The principle remains beautifully simple:
Borrow where it's cheap → Invest where it's not → Keep the difference.
Instead of borrowing Yen, people can now borrow digital assets like USDC or SOL on-chain to purchase higher-yielding instruments like liquid staking tokens (LSTs), restaking tokens, and LP positions.
All transactions happen transparently and instantly on a blockchain, significantly improving speed, efficiency, and accessibility.
How can YOU do it right now
Imagine you start with $10,000 in JitoSOL, earning about 10% staking yield annually. Without leverage, you'd make $1,000 yearly—not bad, but not game-changing.
With leverage, things get exciting:
Deposit your $10,000 JitoSOL as collateral on a lending protocol (like Kamino, Drift, MarginFi).
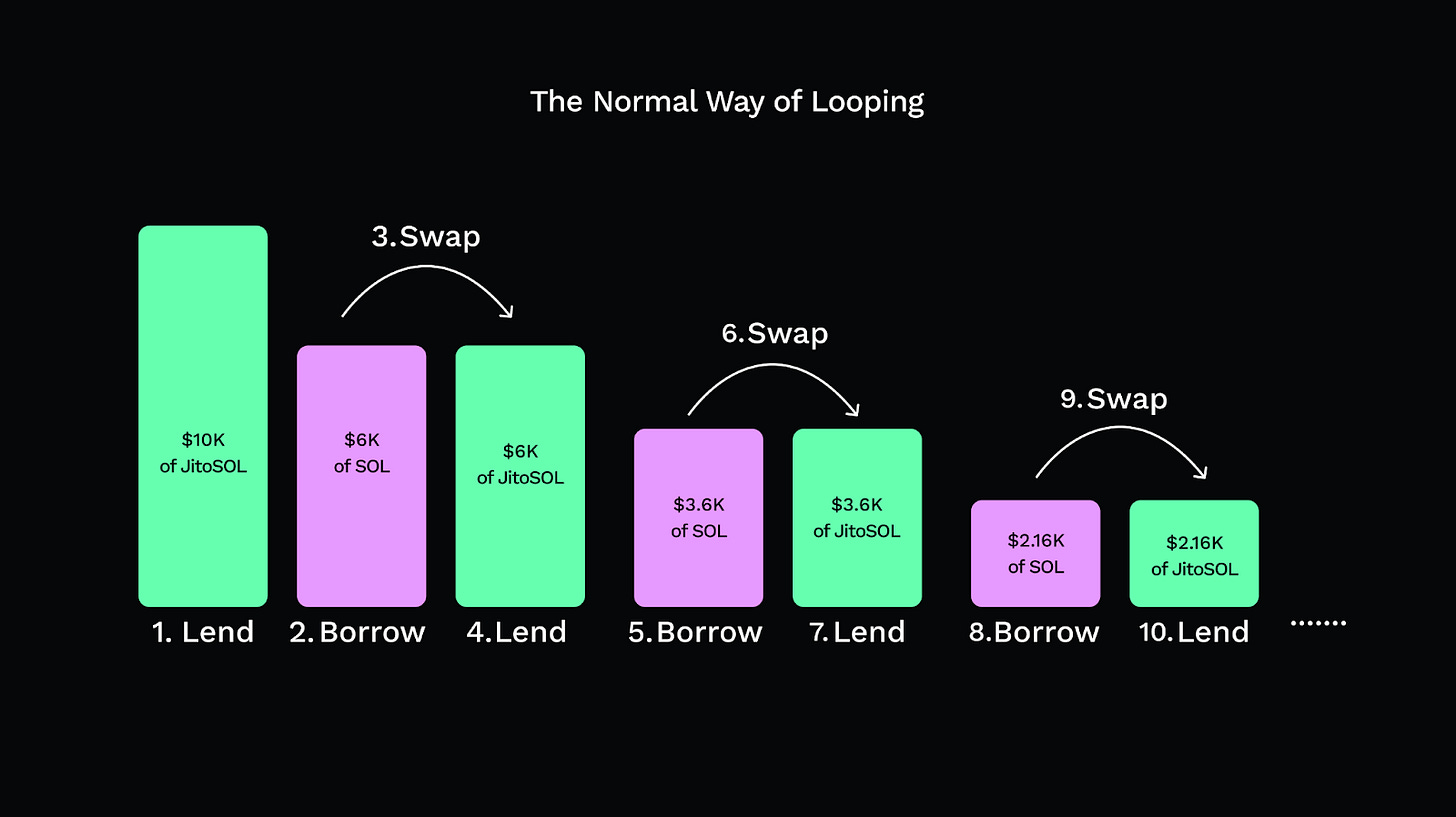
Borrow $6,000 SOL at a ~7.5% rate, swap it back to more JitoSOL, and deposit it again—this is called "looping".
Repeat this a few times.
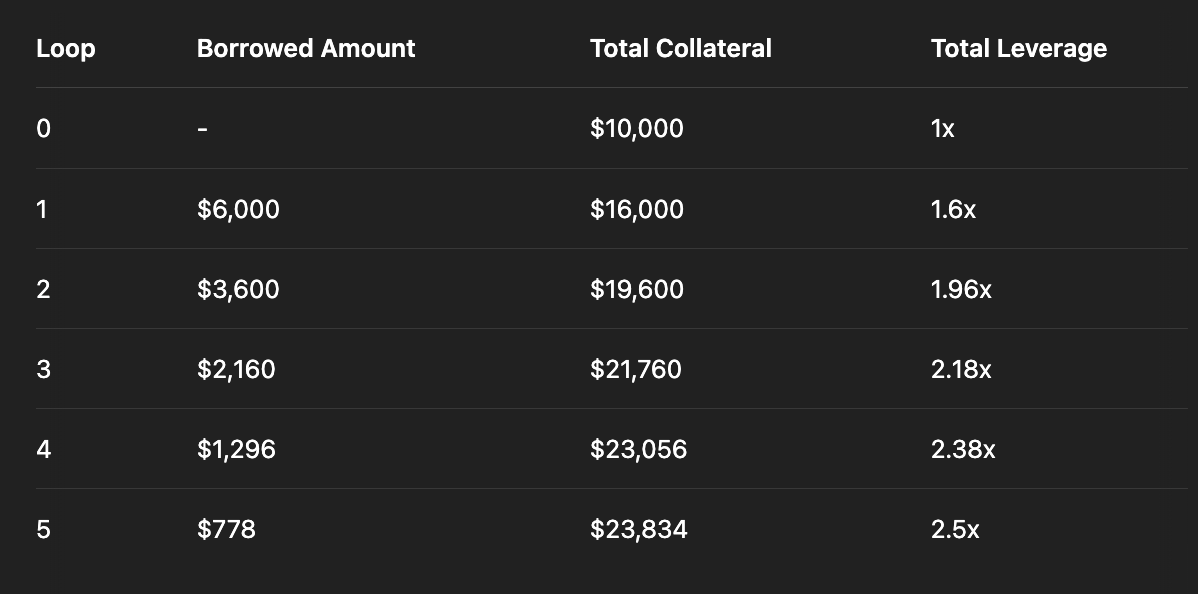
Let's break down an example of how this works in DeFi today:
You start with $10,000 of JitoSOL as collateral and lend it.
Loop 1:
Borrow $6,000 in SOL (60% LTV), swap to JitoSOL, and deposit.
→ Total collateral: $16,000
→ Leverage: 1.6XLoop 2:
Borrow $3,600 (60% of the new $6,000), swap to JitoSOL, deposit.
→ Collateral: $19,600
→ Total borrow: $9,600
→ Leverage: 1.96XLoop 3:
Borrow $2,160, swap and deposit.
→ Collateral: $21,760
→ Borrow: $11,760
→ Leverage: 2.18XLoop 4:
Borrow $1,296, swap and deposit.
→ Collateral: $23,056
→ Borrow: $13,056
→ Leverage: 2.38XLoop 5:
Borrow $777.60, swap and deposit.
→ Collateral: $23,833.60
→ Borrow: $13,833.60
→ Leverage: 2.5X
Final Position:
Total JitoSOL Collateral: ~$23,833.60
Total SOL Debt: ~$13,833.60
Leverage: 2.5x
Net Yield (assume 10% JitoSOL Staking APY, 7.5% borrow rate):
Earnings: 10% × $23,833.60 = $2,383.36
Costs: 7.5% × $13,833.60 = $1,037.52
Net profit = $1,345.84/year
Effective APY: 13.46% on your initial $10,000
Right now, many sophisticated users are already doing this manually – executing 10-15 separate transactions in a row to achieve the same result. They deposit, borrow, swap, deposit again... and repeat. At each step, they're paying fees and suffering slippage, all while managing complex liquidation risks across multiple platforms.
The strategy works, but the current implementation is far from optimal. That's where Asgard comes in.
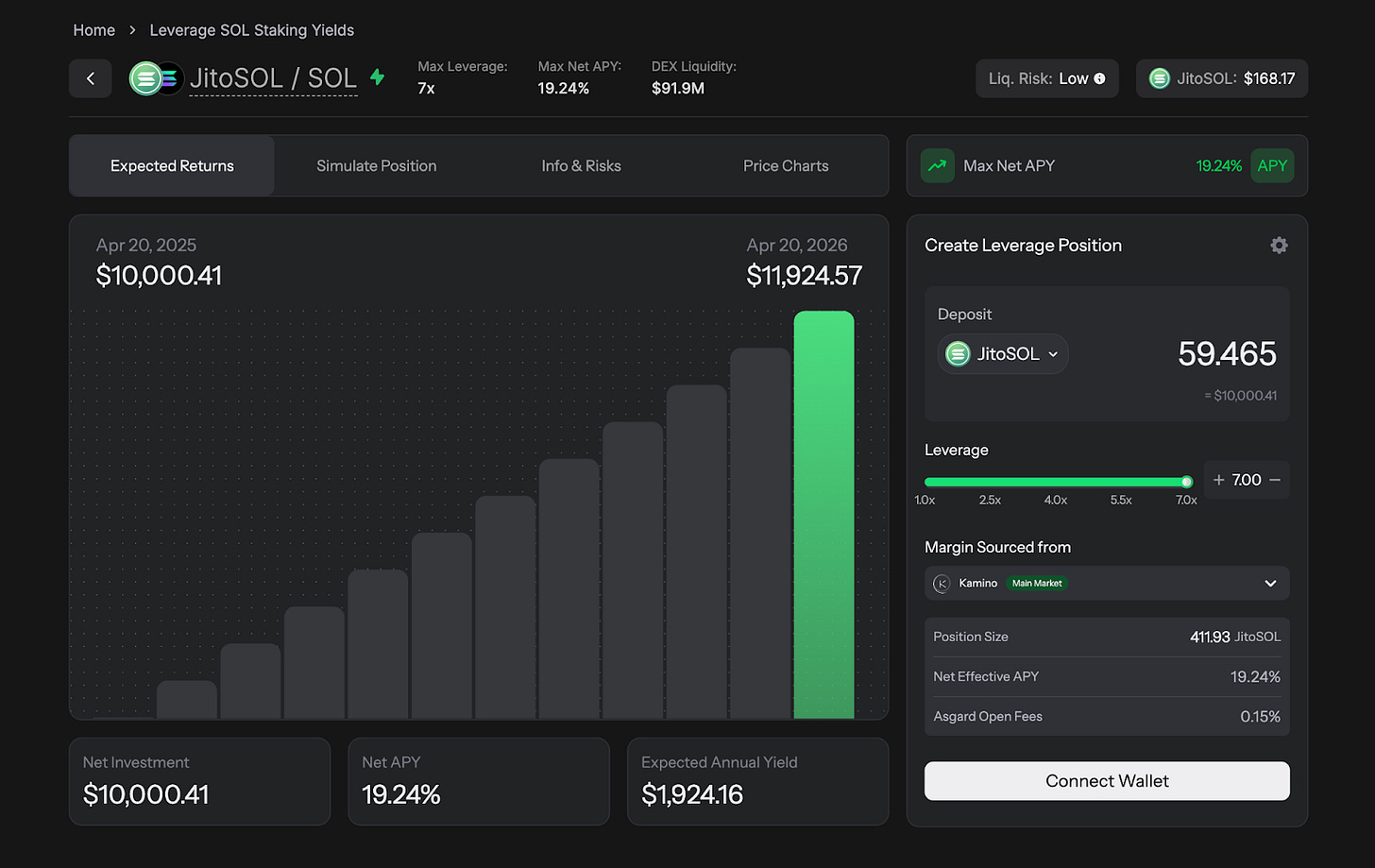
Asgard is supercharging yields.
What if we tell you, all of this can be done in one click on Asgard? Asgard handles the borrowing, conversion, and position management automatically – no need to juggle multiple platforms or execute complex transactions.
Just as the original carry trade gave large institutions the ability to deploy billions across global markets with ease, Asgard now puts that same financial power at your fingertips. What once required massive trading desks, prime brokerage relationships, and sophisticated treasury operations is now available to anyone with an internet connection.
But isn’t leverage risky?
What makes this strategy particularly safe is that JitoSOL and SOL are highly correlated assets. Unlike leveraging SOL against USDC (where a drop in SOL price could quickly lead to liquidation), the JitoSOL/SOL pair moves almost in tandem. JitoSOL is essentially SOL plus staking rewards, so the liquidation risk is dramatically reduced.
That's the power of leverage applied to yields. You've more than tripled your returns without taking on significant market directional risk.
Even if the market drops, both your collateral (JitoSOL) and your debt (SOL) decrease in dollar terms together, keeping your position relatively stable. This correlation protection is what makes yield-focused leverage strategies much safer than traditional directional leverage.
As long as the yield on JitoSOL stays higher than your borrowing cost, you're capturing that spread efficiently, with minimal worry about market volatility.
Asgard's Leverage Yield Aggregator turns this complex leverage strategy into a single click.
One-Click Execution: What currently requires dozens of transactions occurs in one click without any human-induced errors, slippage issues, MEV, and arbitrages.
Whole Ecosystem Access: Instead of being limited to one market, deploy leverage across the full spectrum of Solana's DeFi ecosystem
Maximum Capital Efficiency: Connect to Marginfi, Kamino, drift, Save and more—giving you access to the deepest liquidity and best rates across Solana
Exposure to Points: Earn points and incentives from underlying protocols (boosting your potential future airdrops).
Risk Management: Sophisticated correlation monitoring and position management to prevent liquidations.
Unlike perpetual futures, which create synthetic exposure, here you deal with real assets and real yield. When you leverage JitoSOL through our platform, you're still earning actual staking rewards – just multiplied by your leverage factor.
The beauty of DeFi is there's room for multiple approaches. Just like Wall Street developed dozens of variations on the carry trade, we're seeing the same evolution on-chain. More tools mean more opportunities for yield-hungry investors.
A New Financial Engine Built for Everyone
For decades, carry trades were a secret weapon of Wall Street's elite. If you didn't have a dedicated trading team, deep banking relationships, and millions in capital, you were locked out. The wealth-building strategies used by hedge fund titans felt impossible for ordinary investors to access—until now.
At Asgard, we've taken the same powerful strategies that made institutions billions and distilled them into tools anyone can use. With one click, you harness the strength of Wall Street-grade financial strategies, turbocharged by DeFi's transparency, speed, and fairness.
The future of finance isn’t about chasing risky 100x bets or gambling on market swings. It’s about building smarter, safer, and more sustainable ways to grow your wealth. Just as the Yen carry trade defined an era of institutional investing, Asgard is pioneering an entirely new financial landscape—one where the same powerful principles drive financial freedom for everyone.
Because when you pair intelligent leverage with reliable, high-yield assets, you get more than just profits. You unlock a new financial reality.
Try Asgard's beta today: beta.asgardfi.com
Thanks for Reading
Hope you found this breakdown helpful — and that carry trades make a lot more sense now (especially how you can run one yourself in DeFi).
If you enjoyed the read or learned something new, consider sharing it with a friend or posting it on crypto Twitter. We’re building in public, and every bit of feedback or reach helps us make Asgard even better.
We’d love to hear your thoughts, experiments, or questions. Drop us a line on Twitter.
Further Reading & References
Commonfund. (2024). How Long Can the Yen Carry Trade Carry On?
J.P. Morgan Private Bank. (2024). Amid rate cuts, do carry trades still work.
Finimize (2024). Yen-Funded Carry Trade Unwind Only Halfway Done, Says UBS.
Singh Bhaisora, S. (2024). What is the Japanese Yen Carry Trade? Impact on India & Global Markets. Wright Research.
Tolan, R., Owens, J., & Lica, V. (2022). The Carry Trade and Global Imbalances. Student Economic Review Vol. XXXVI.
Zerodha Varsity. (2024). JPY-USD: The Great Carry Trade. Zerodha Connect.